What are "greenhouse gases?" The transparent windows of a greenhouse (or a car parked in the sunlight) transmit the warming visible rays of the sun, prevent the resulting warm air from leaving, and hence maintain a warmer environment inside than outside the structure Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation and trap its heat in the atmosphere, creating a greenhouse effect that results in global warming and climate change Many gases exhibit these greenhouse properties Some gases occur naturally and are also produced by human activities Some, such as industrial gases, are exclusively human made › en español Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping Longlived gases that remain semipermanently in the atmosphere
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
Greenhouse gases meaning
Greenhouse gases meaning- Greenhouse gas emissions from electricity have increased by about 12 percent since 1990 as electricity demand has grown and fossil fuels have remained the dominant source for generation To learn about projected greenhouse gas emissions to , visit the US Climate Action Report 14 (310 pp, 23 M, About PDF)Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor;When we talk about greenhouse gases, we're referring to carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride Join us on social!However, too many greenhouse gases can cause the temperature to increase out of control Such is the case on Venus where greenhouse gases are abundant and the average temperature at the surface is more than 855 degrees Fahrenheit (457 degrees Celsius) You might hear people talking about the greenhouse effect as if it is a bad thing
Greenhouse gas Chemical formula Global Warming Potential, 100year time horizon Atmospheric Lifetime (years) Global Warming Potential and Atmospheric Lifetime for Major Greenhouse Gases;Many greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and nitrous oxide, while others are synthetic Those that are manmade include the chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and Perfluorocarbons (PFCs), as well as sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6 ) Atmospheric concentrations of bothCarbon dioxide Water Vapour Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases Sources As greenhouse gases are essential for the existence of life, they are present in the atmosphere in a trace amount Natural sources of GHGs are volcanos, respiration by living organisms, decay and combustion of organic matter, etc
Greenhouse gas greenhouse gas Methane Methane (CH4) is the second most important greenhouse gas CH4 is more potent than CO2 because the radiative forcing produced per molecule is greater In addition, the infrared window is less saturated in the range of wavelengths of radiation absorbed by CH4, so more molecules may fill in the regionGreenhouse gas definition 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Learn moreGreenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil, and natural gas The largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and Russia



Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Transport In Europe European Environment Agency




How Are Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases By The Eu Evolving
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse Without carbon dioxide, Earth's surface would be some 33 °C (59 °F) coolerGreenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents Greenhouse gases absorb reflected solar energy, making the Earth's atmosphere warmer A lot of the sun's energy reaches the ground directly, and a portion is reflected by the ground back into space
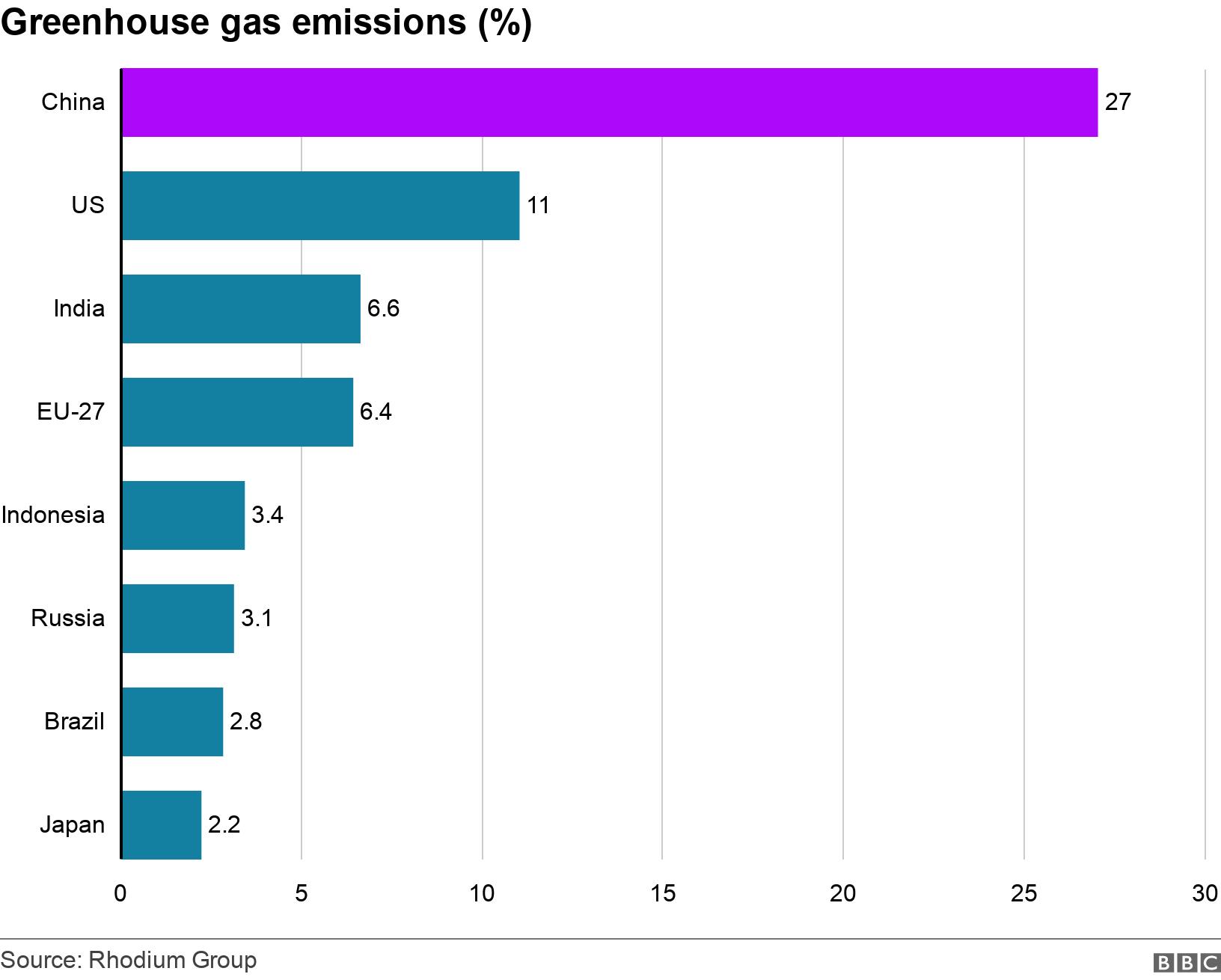



Report China Emissions Exceed All Developed Nations Combined c News




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
The term "greenhouse gases," or GHGs, covers a wide variety of gases that, once they are released into the atmosphere, trap the sun's heat When the sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and trapped in the lower atmosphere, heating the Earth The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gases Apple supports a clean energy standard proposed by the Biden administration that would eliminate greenhouse gases from power plants by 35, said Lisa Jackson, Apple's VP of environment, policy




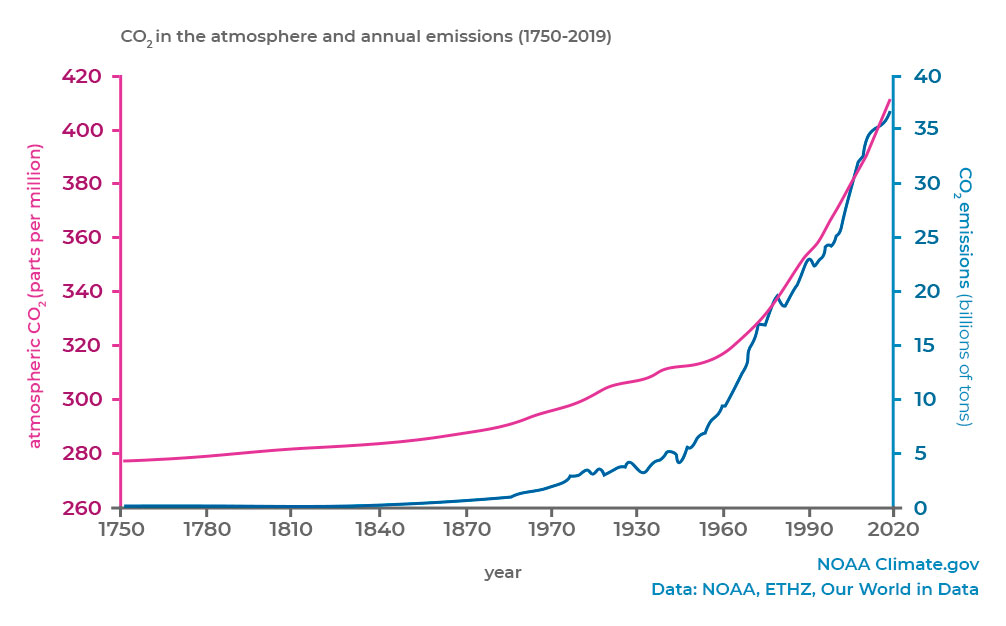
Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
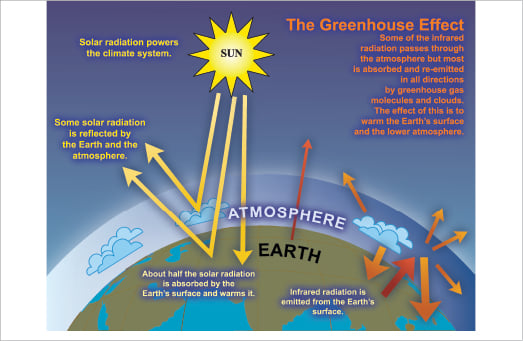



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases Greenhouse gases are not aGreenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere When energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as lightGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming one




Indicator Greenhouse Gas Emissions Umweltbundesamt




Climate And Greenhouse Effect Umweltbundesamt
"Dumping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere makes the atmosphere more humid And since water vapor is itself a greenhouse gas, the increase in humidity amplifies the warming from carbon dioxide" Specifically, the team found that if Earth warms 18 degrees Fahrenheit, the associated increase in water vapor will trap an extra 2 Watts ofAny of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does not



On Farm Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Practices




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons
Since the Industrial Revolution, rising emissions of greenhouse gases—including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and others—have been the driving force behind climate change Who is responsible for emitting the most greenhouse gases? Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight Unlike those more abundant gases though, greenhouse gases are not transparent to heat (longwave infrared radiation) The sunwarmed surface of Earth radiates heat day and night The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect




The Greenhouse Gases Airclim




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
As a greenhouse gas, the higher concentration of water vapor is then able to absorb more thermal infrared energy radiated from the Earth, thus further warming the atmosphere The warmer atmosphere can then hold more water vapor and so on and so on This is referred to as aGreenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which makes the Earth warmer People are adding several types of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and each gas's effect on climate change depends on three main factorsThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)



Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Proterra Foundation




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
Learn more about climate change and discover ways to take actionThe answer may not be as clear as one might assume, because the top emitters change depending on how the data is collected and what A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in



Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gas emissions Germany 'set for biggest rise in greenhouse gases for 30 years' Increase means country will slip back fromGreenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the EarthHuman activities are responsible for almost all of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere over the last 150 years 1 The largest source of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities in the United States is from burning fossil fuels for electricity, heat, and transportation




China Aims To Cut All Greenhouse Gases By 60 Researcher Says Caixin Global
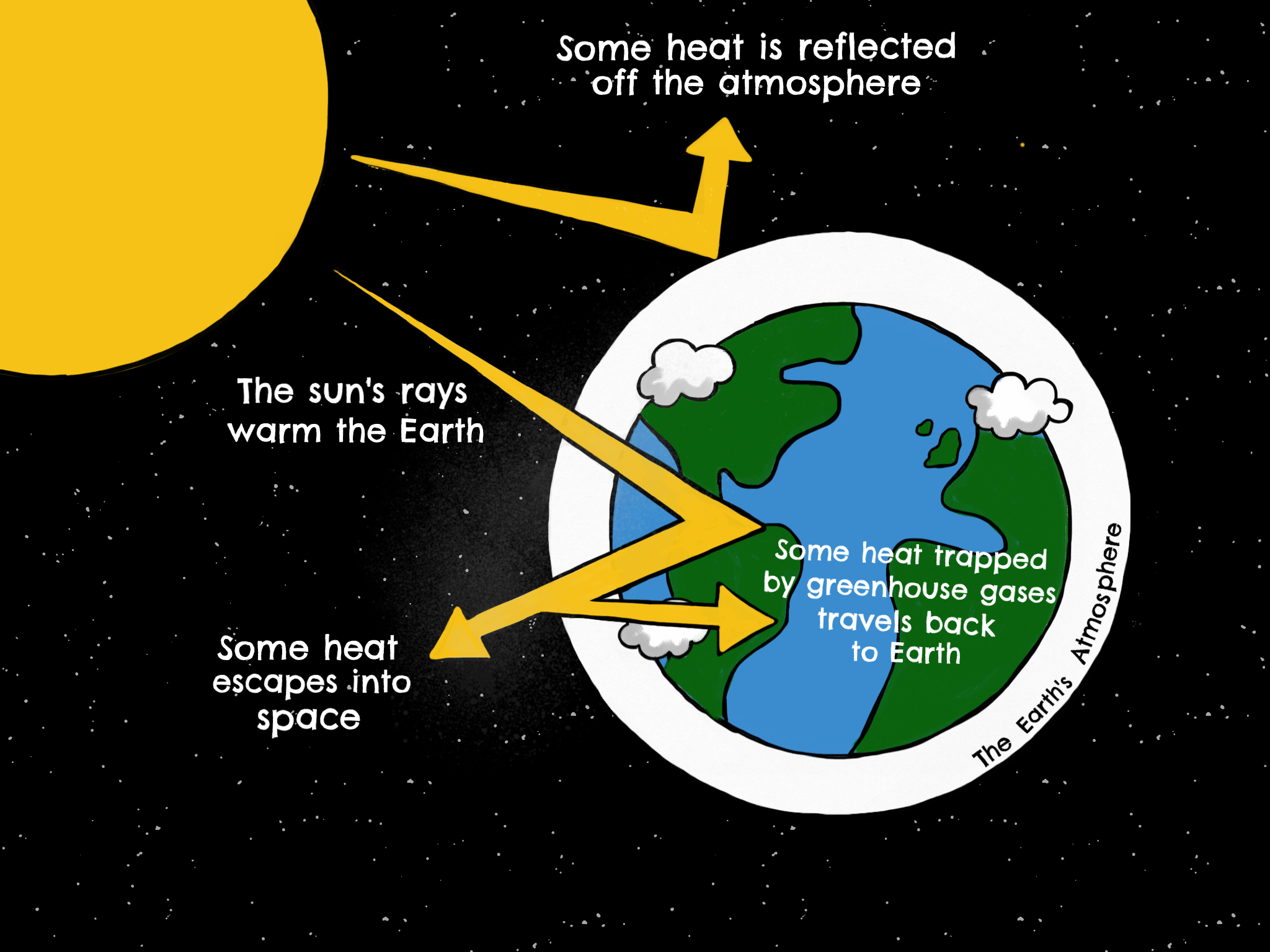



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change
Carbon Dioxide CO2 1 100* Methane CH4 25 12 Nitrous Oxide N2O 265 121 Chlorofluorocarbon12 (CFC12) CCl2F2 10,0 100 Hydrofluorocarbon23 (HFC23) CHF3



1



Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects The News Motion




Greenhouse Gas Emissions On A Global Level And Seven Large Countries Download Scientific Diagram



Chart China Beats U S Europe In Combined Greenhouse Gases Statista
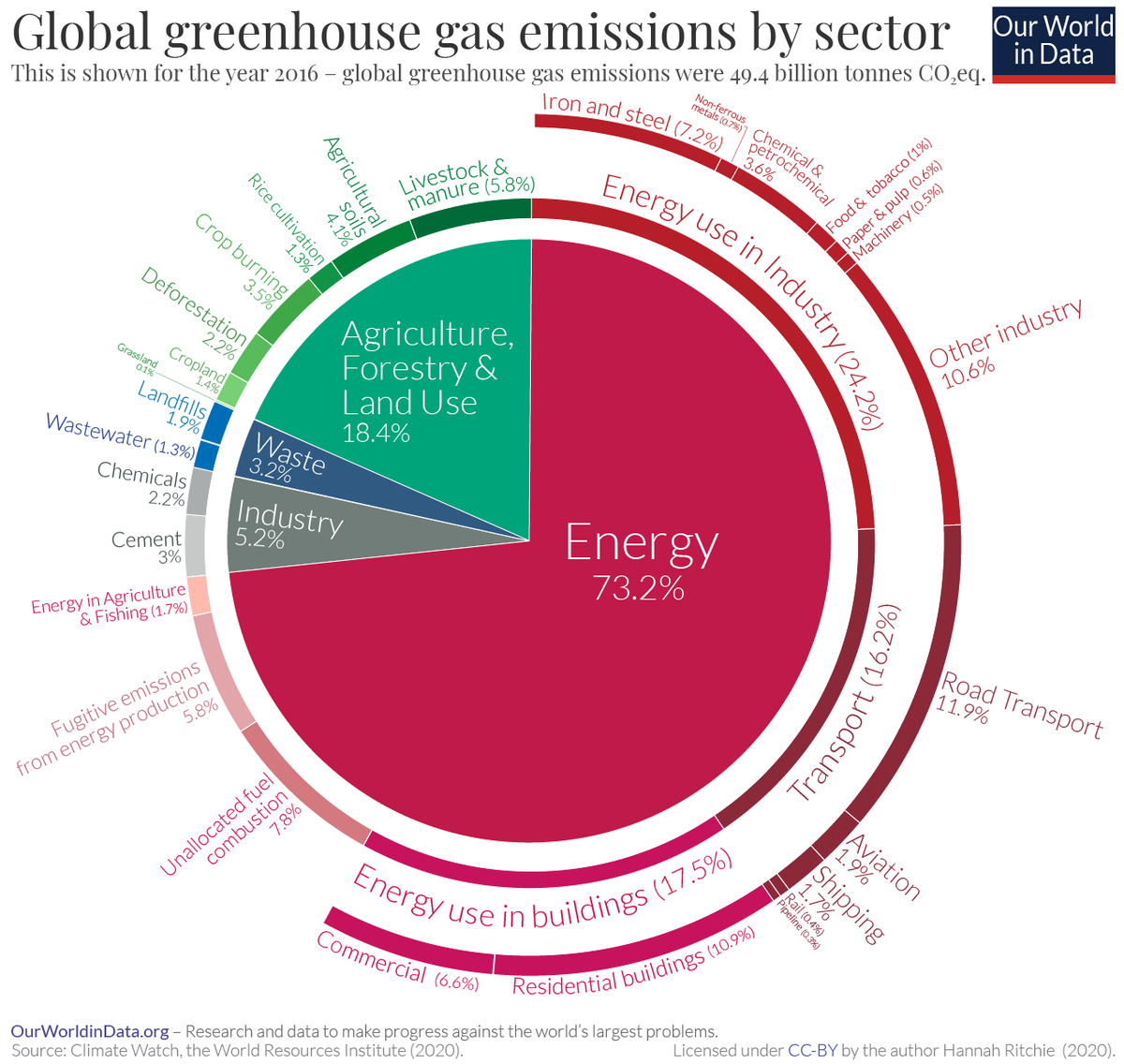



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect How Does Climate Change Work




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate Change Posts Facebook
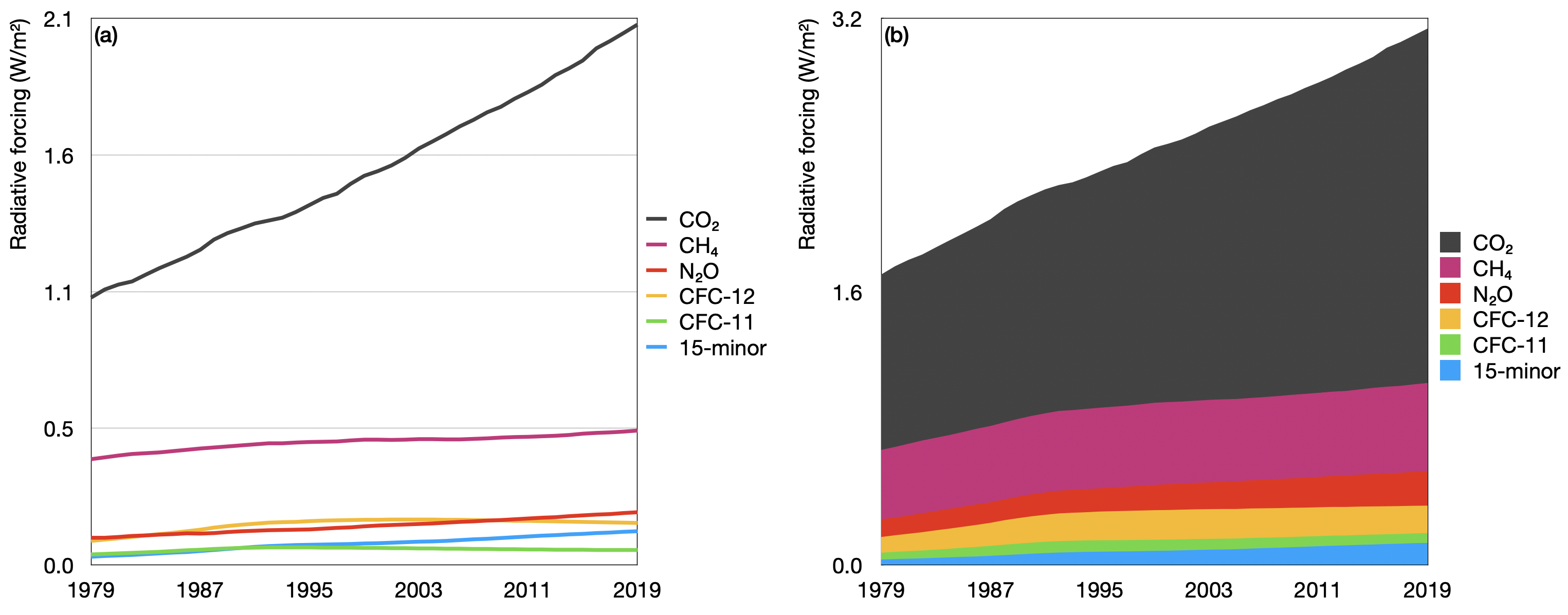



Greenhouse Gas Emissions
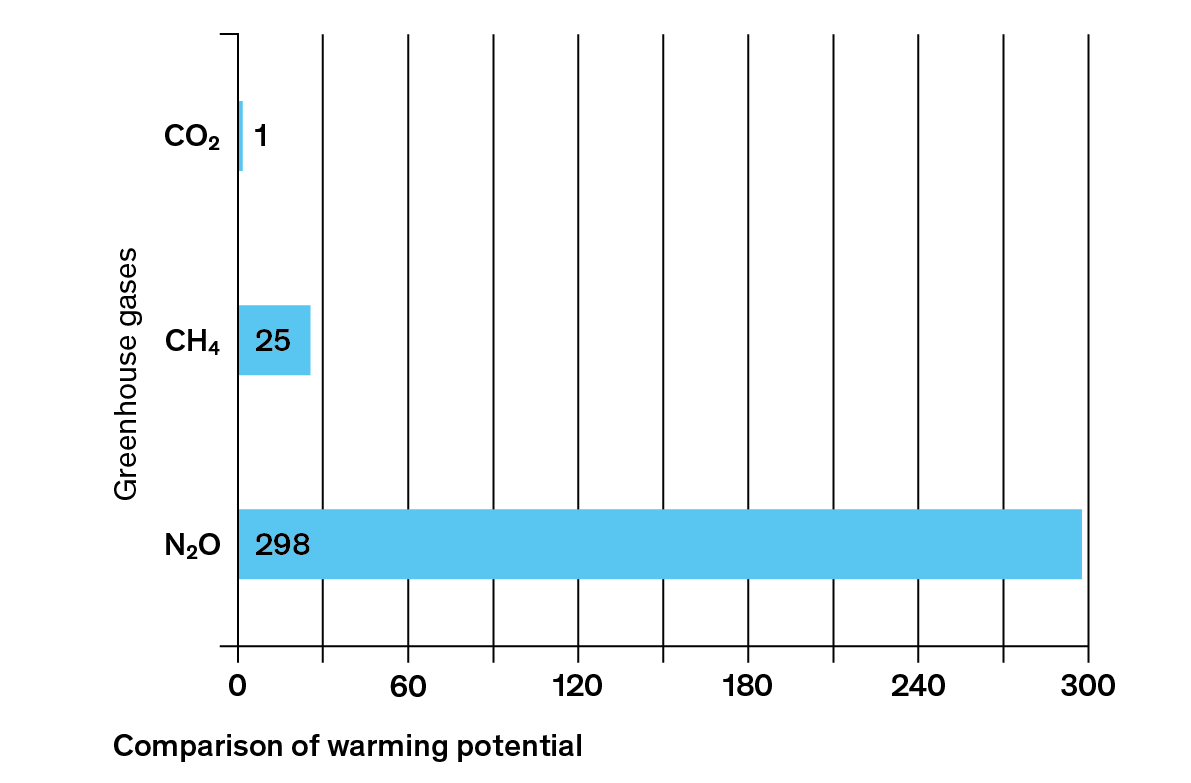



What Are Greenhouse Gases Myclimate




Banning The Super Greenhouse Gas Environment All Topics From Climate Change To Conservation Dw 17 10 16




Greenhouse Gases Are Components Of The Atmosphere That Contribute To The Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
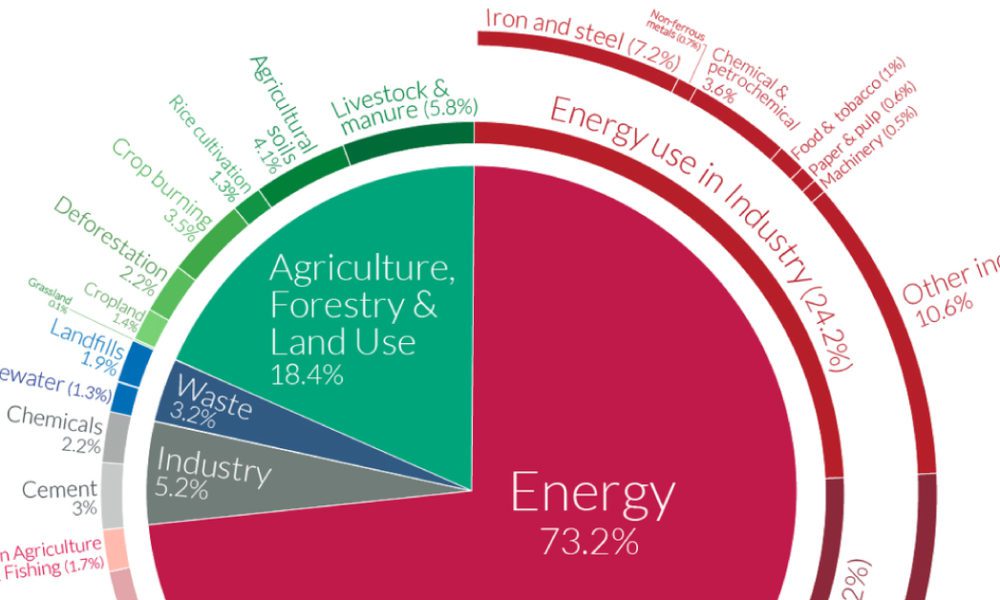



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




The Greenhouse Gases The Environment Monitor



The 5 Most Abundant Greenhouse Gases And Where They Come From Greenbuzz Berlin E V




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Institute For Atmospheric Physics Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus



Greenhouse Gases
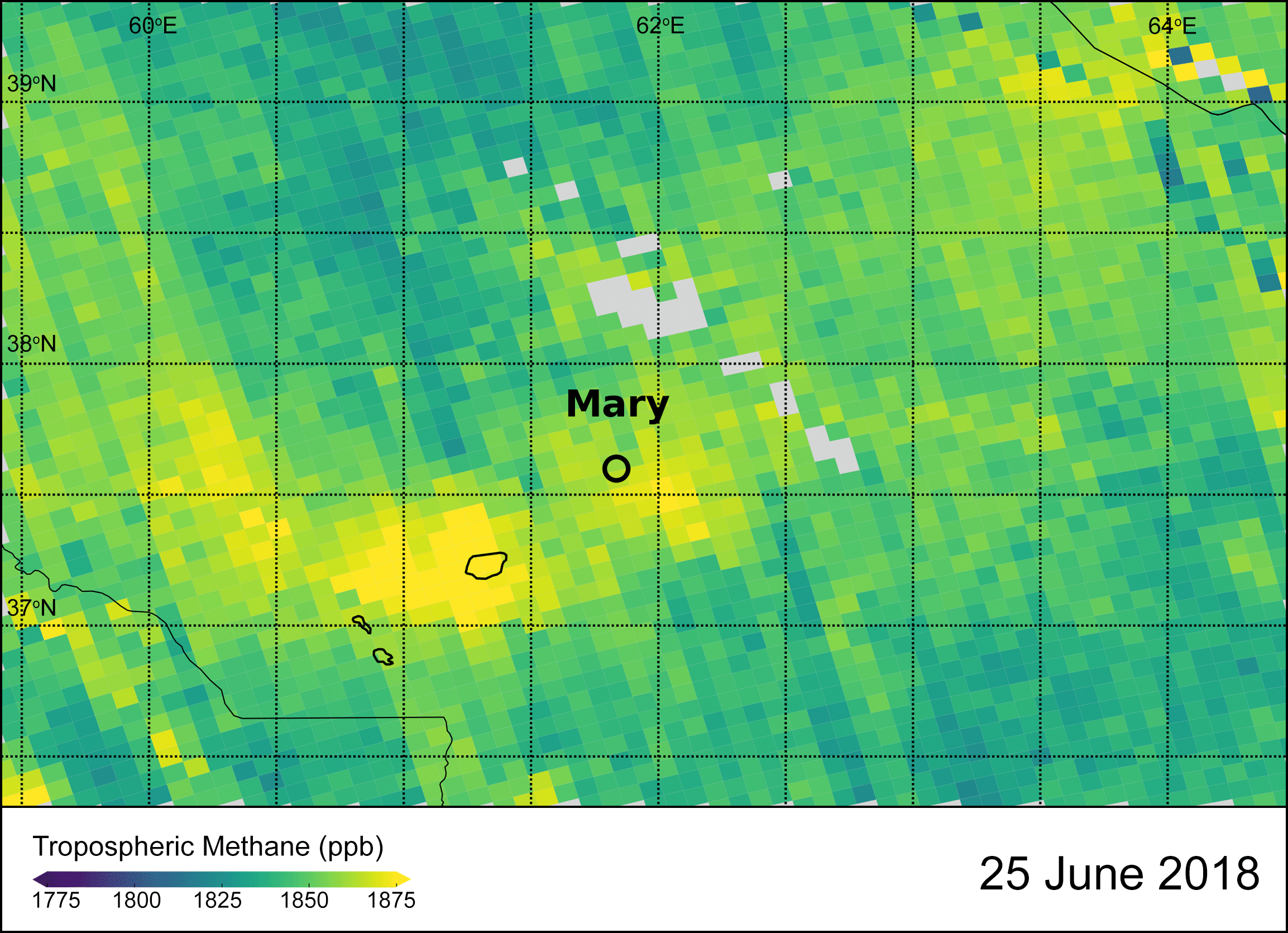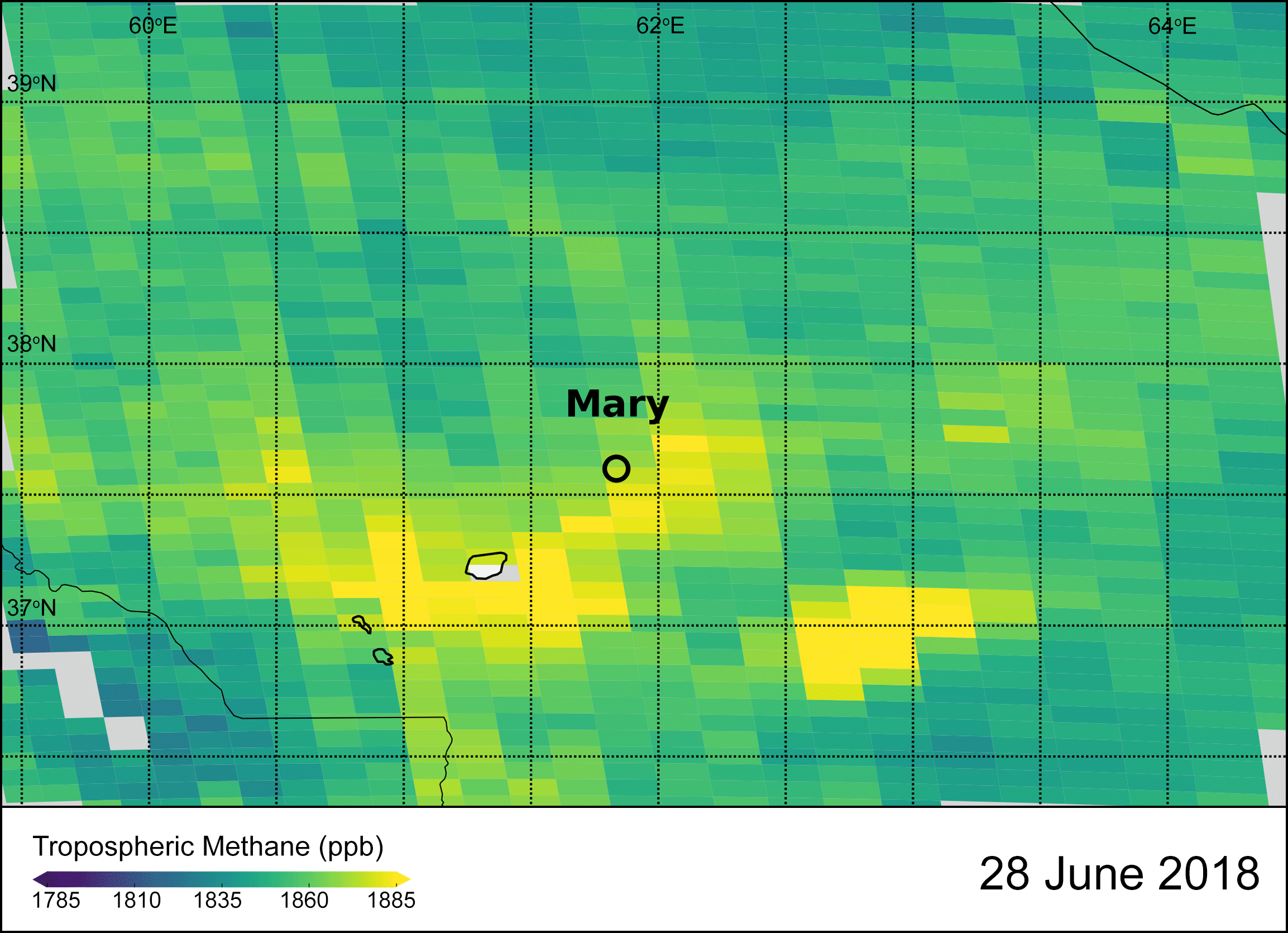



Esa Satellites Providing Clear Picture Of Greenhouse Gases



Cilab Greenhouse Gases Effect On Global Warming




Greenhouse Effect Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Design Emission




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gases




France Greenhouse Gas Emissions Decreased By 16 9 From 1990 Levels Climate Scorecard




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
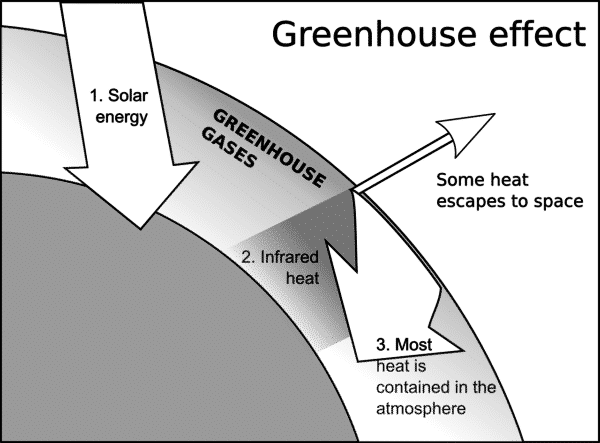



What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub




What S The Deal With Greenhouse Gases Emissions And The Environment Futurelearn




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist




Uk Agricultural Sector Ghg Emissions 1990 19 Statista
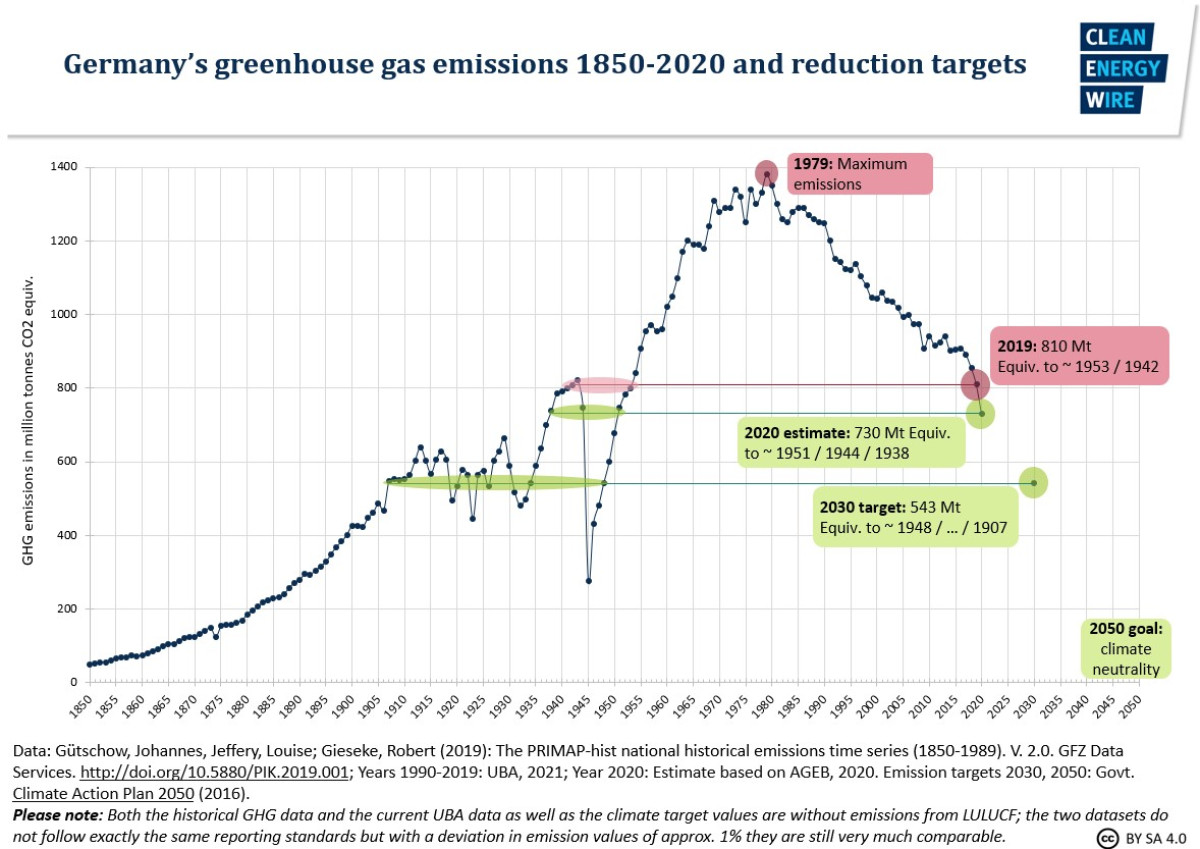



Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire
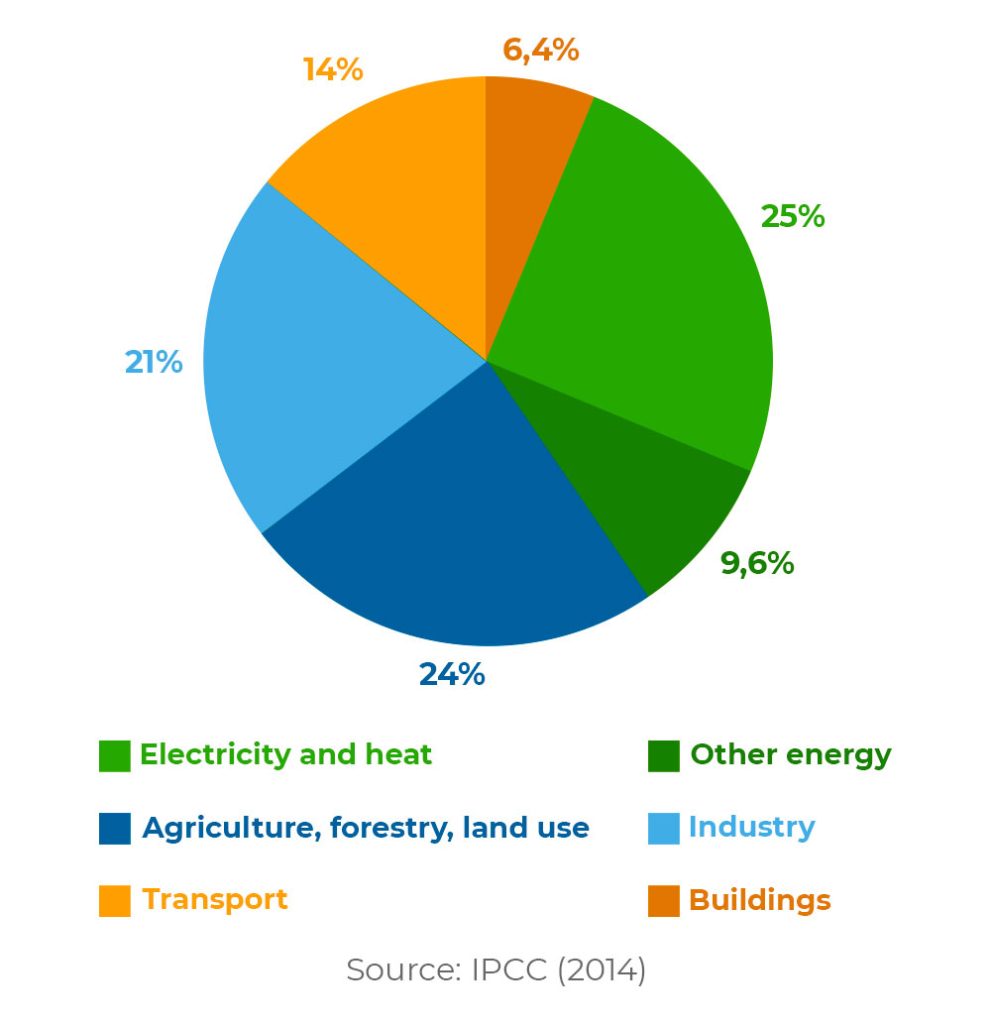



Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Proterra Foundation




Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Models For Kids Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Methane




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




Dark Greenhouse Gases Pie Chart Template




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




1 Major Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Contributions By Various Sectors Download Scientific Diagram




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Gmd The Shared Socio Economic Pathway Ssp Greenhouse Gas Concentrations And Their Extensions To 2500




190 Increase In Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Turkey Since 1990 Climate Scorecard




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



1



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
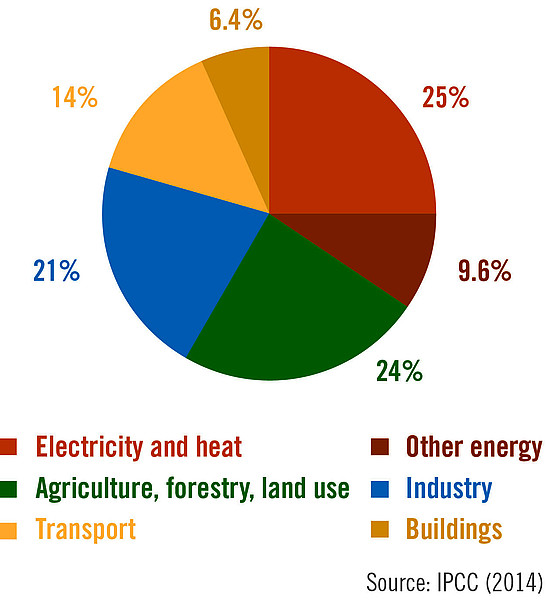



Climate And Energy




Innovative Technologies Enable Transition Away From Sf6 Greenhouse Gases
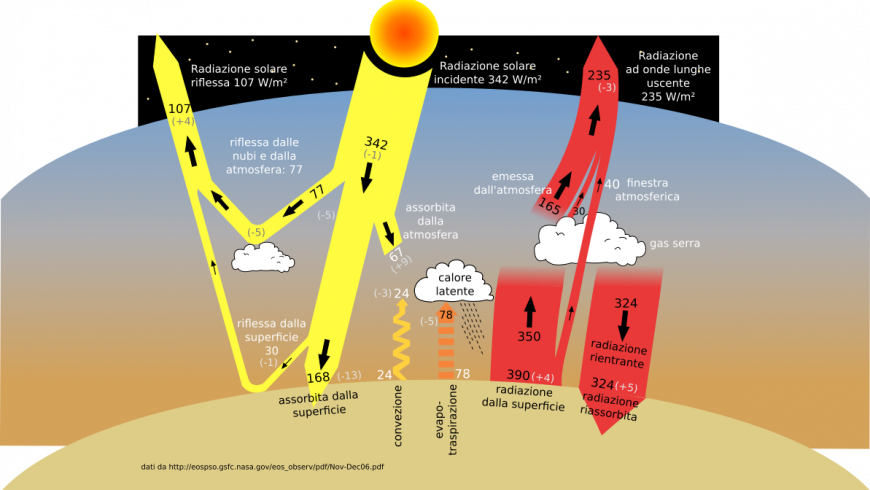



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions
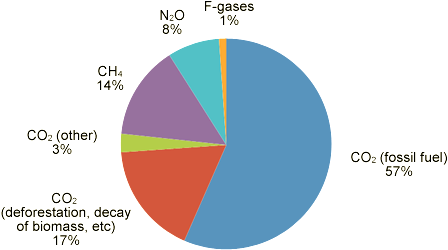



Energyland Greenhouse Gases
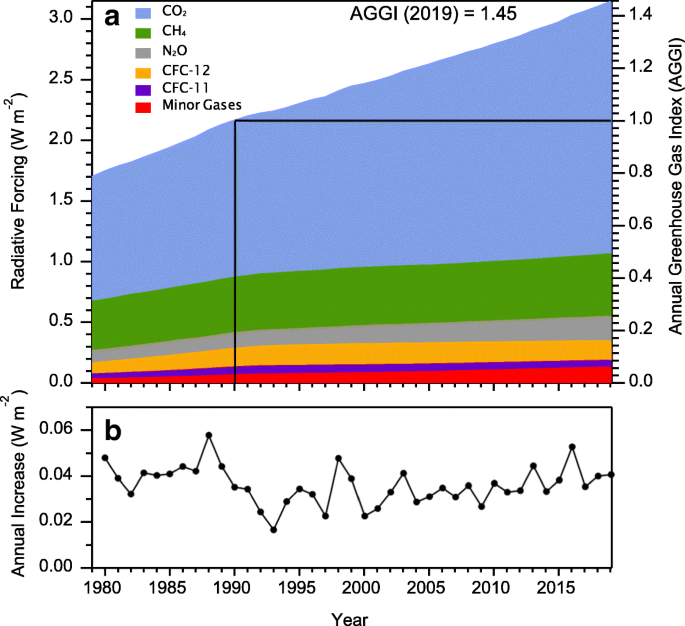



Observations Of Greenhouse Gases As Climate Indicators Springerlink




Impact Of Snow On Soil Greenhouse Gases



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau




Tool For Calculating Greenhouse Gases Ghg In Solid Waste Management Swm Ifeu Ggmbh




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Q Tbn And9gcqob5akx 2xithdb3seiv5jyef5ryrbg3xvzguy4p57lypo5m0p Usqp Cau
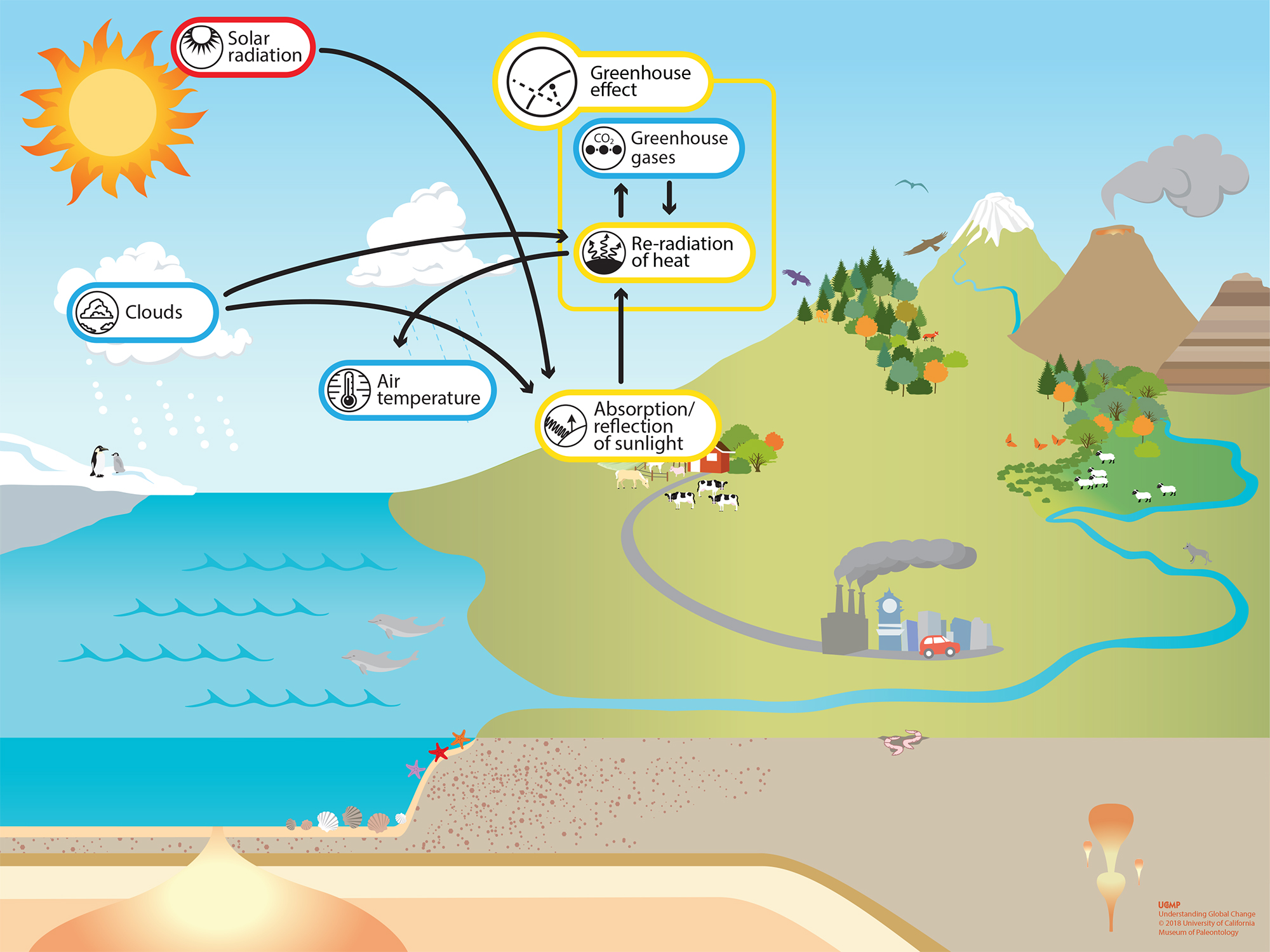



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
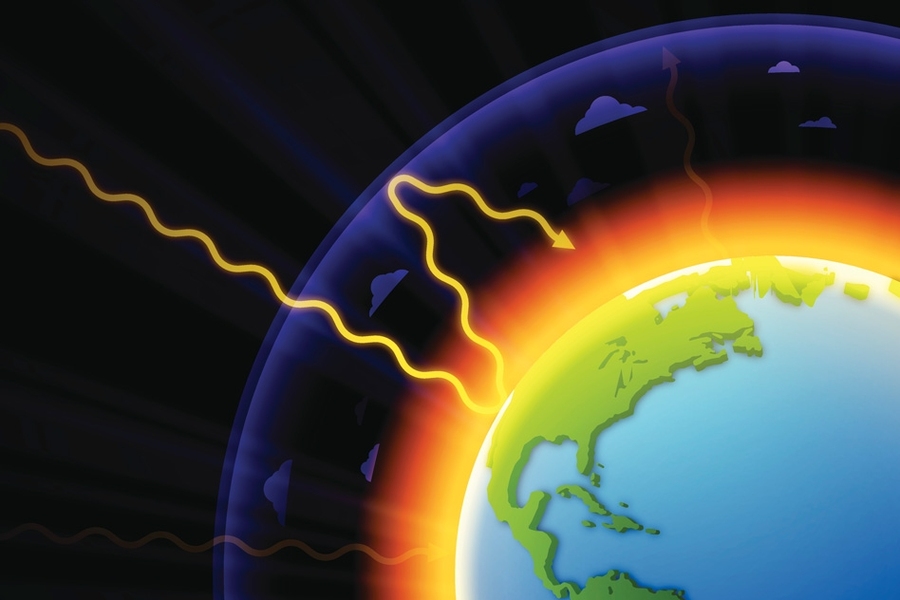




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
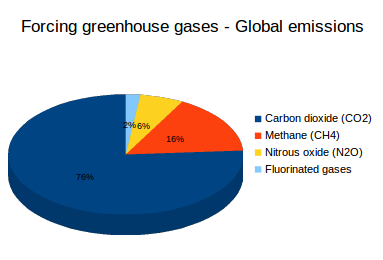



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact
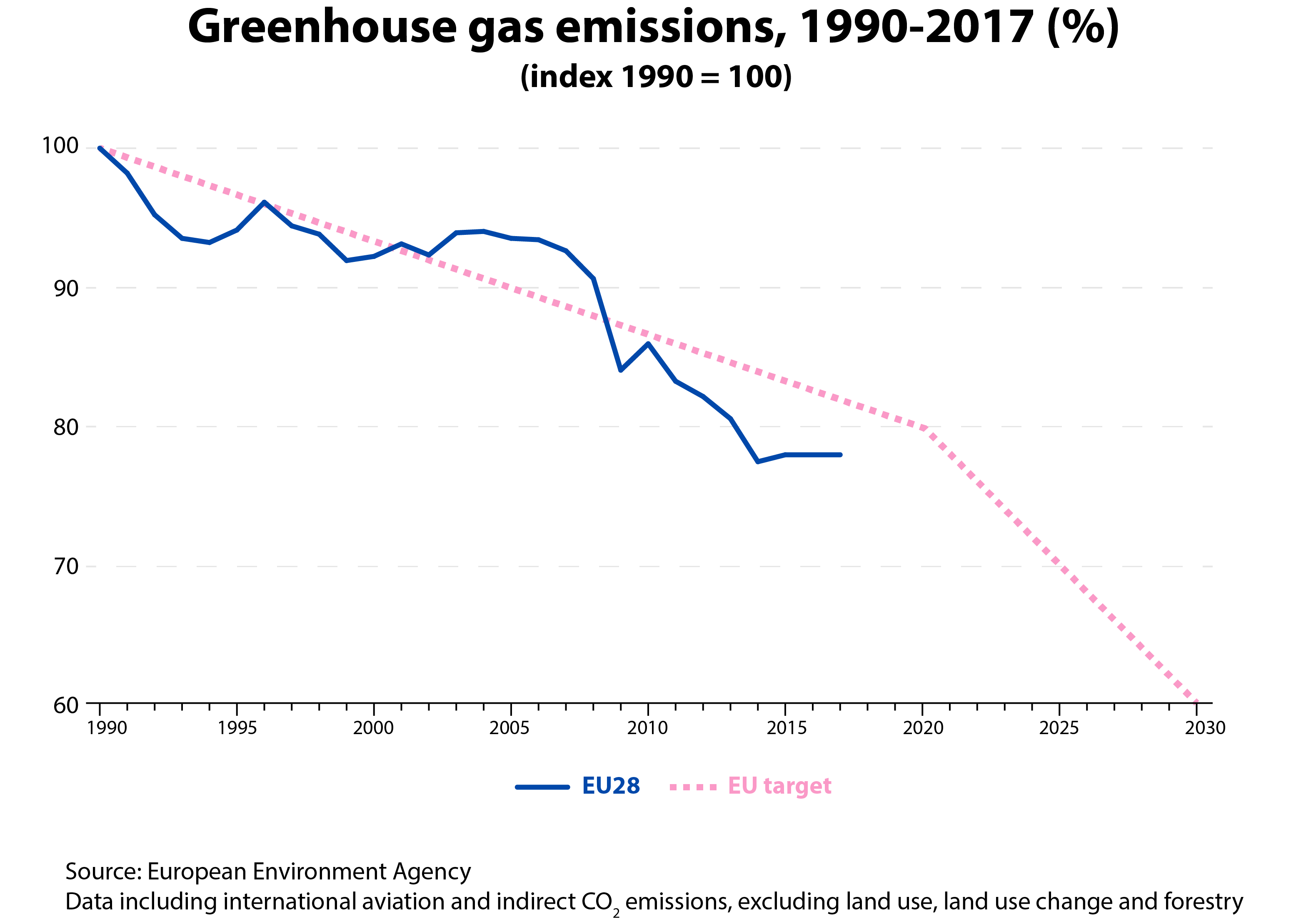



How Are Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases By The Eu Evolving




Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire




The Greenhouse Effect Cool Australia



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja




Greenhouse Gases The Australian Museum




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons




Trends In Global Co2 And Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions Summary Of The 17 Report Pbl Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency
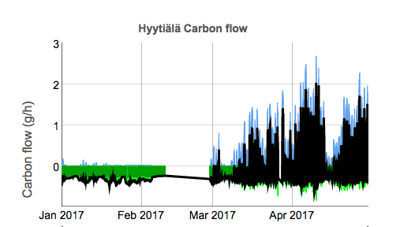



Impact Of Snow On Soil Greenhouse Gases
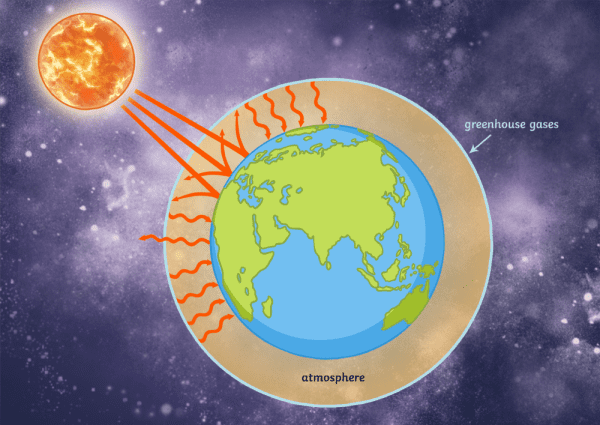



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Greenhouse Gases 101 Ben Jerry S




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Esa Satellites Providing Clear Picture Of Greenhouse Gases
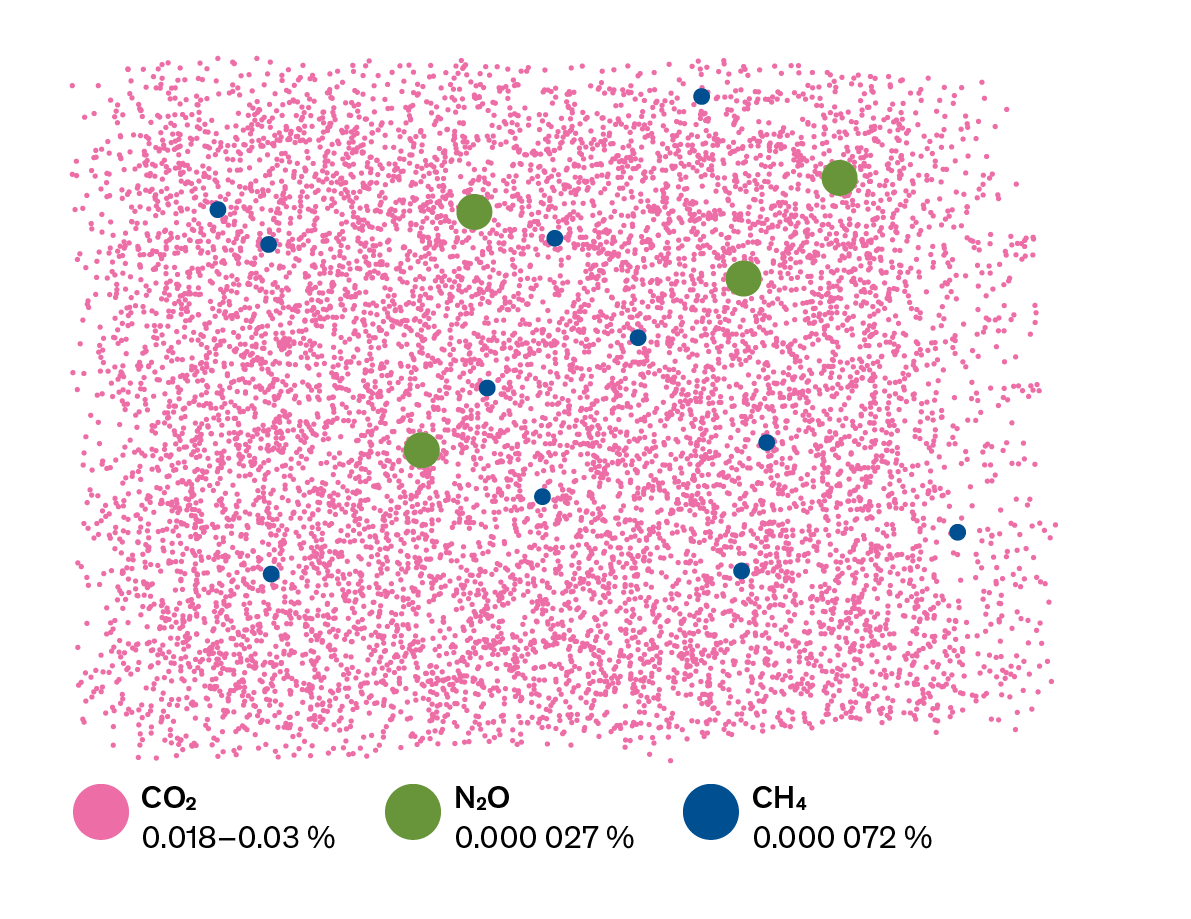



What Are Greenhouse Gases Myclimate
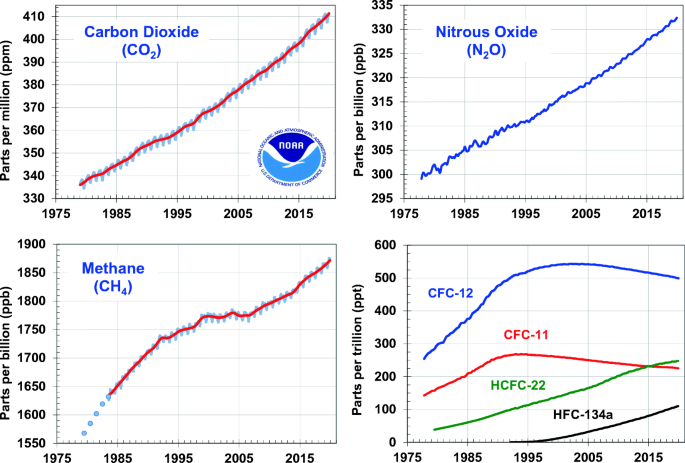



Observations Of Greenhouse Gases As Climate Indicators Springerlink
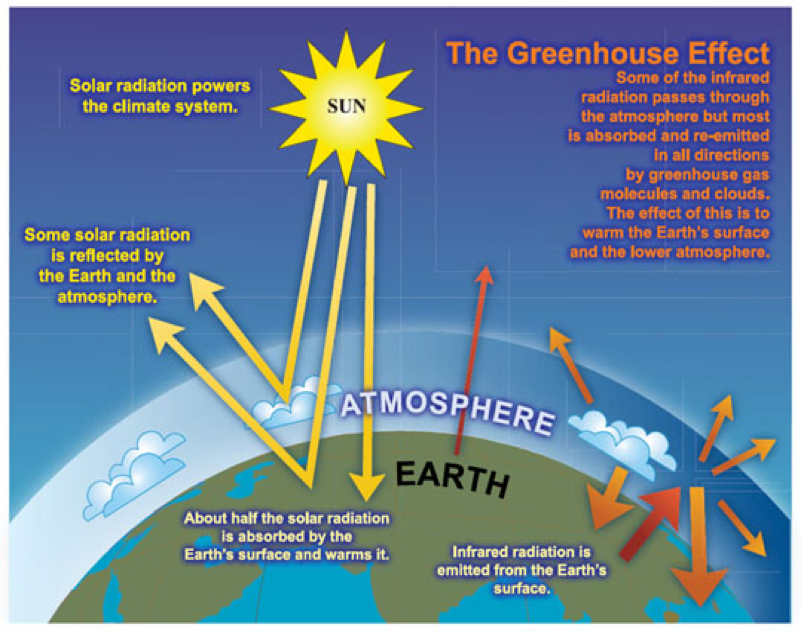



Greenhouse Gas Reduction




Geolog 1 Years Of The Greenhouse Effect
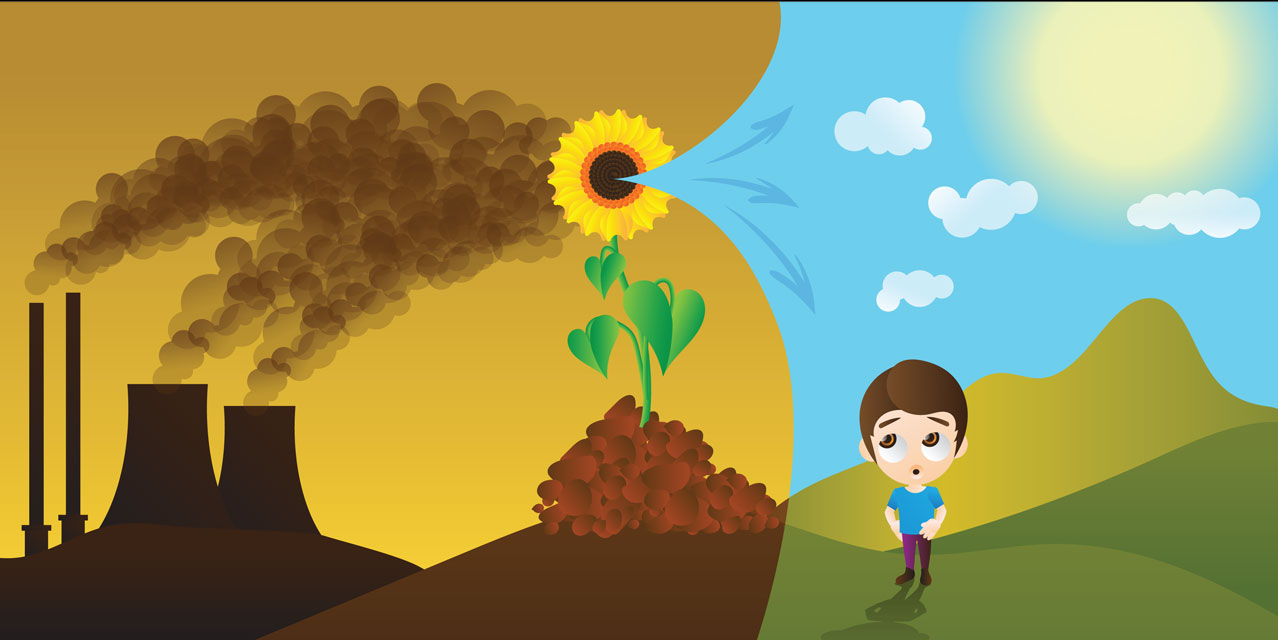




Removing Harmful Greenhouse Gases From The Air Using Energy From Plants Frontiers For Young Minds




Where Do Greenhouse Gases Come From Pela Case




1zrlfbmrqd Vwm



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿